Explain the Difference Between a Discrete and a Continuous Metric
In general a continuous variable is one that is measured not counted. If a random variable takes all possible values between certain given limits it is called as continuous random variable.

Continuous Vs Discrete Data Youtube
With Netica you can choose whether you want a node to represent a discrete or continuous variable.

. Temperature time distance - all are continuous variables. If a random variable takes only a finite or countable number of values it is called as discrete random variable. However one must collect a large amount of discrete data to draw appropriate statistical conclusions as compared to continuous data.
Show activity on this post. Takes any measured value within a specific range. R R R.
3Explain the differences between categorical ordinal interval and ratio data. Discrete Random Variable. Height for example is measured.
A discrete variable corresponds to a digital quantity while a continuous variable corresponds to an analog quantity. If you take d x n y n 1 0 d x y. Definition - A continuous variable is a variable that takes on any value within a range and the number of possible values within that range is infinite.
Continuous Random Variable. 1Discrete Data 2Continuous Data Below table illustrates how data type determines which statistical test can be applied in a given scenario. Some common examples of discrete data are the number of students the number of children the shoe size and so on.
Continuous data is measurable. A discrete variable can be graphically represented by isolated points. Some common examples of continuous data are height weight length time temperature age and so on.
What is wrong with my reasoning. Continuous data is data that falls in a continuous sequence. Discrete data refers to specific and distinct values while continuous data are values within a bounded or boundless interval.
Discrete data is counted Continuous data is measured. The difference between discrete and continuous variables is that the former relates to a specific and often simplistic number the value of which has been obtained purely through counting whereas the latter is a progressive changing number that is. Often a variable will be continuous at one scale but discrete on another.
Recall that between any two real numbers there are infinitely many additional real numbers. It is proven that any metric d is continuous. Discrete data is countable while continuous data is measurable.
Data is generally classified into two categories. For example if Y dependent variable is continuous and Xs independent variables are discrete then we can use ANOVA to test means. Takes specific countable values.
Definition - A discrete variable is a variable that takes on distinct countable values. Discrete data and continuous data are the two types of numerical data used in the field of statistics. The difference between discrete and continuous data can be drawn clearly on the following grounds.
A discrete distribution is one in which the data can only take on certain values for example integers. 4In conducting a multiple linear regression analysis an R 2 value of 046 is obtained. Discrete variables have values that are counted.
This shows that this metric is discontinuous. Continuous mathematics deals with real numbers. 2Explain the difference between a discrete and a continuous metric.
There are no gaps in the real number line that continuous math operates on. Water volume or weight. Discrete math deals with sets of items numbers for example that can only contain certain discrete values.
The values of a continuous variable are measured. Discrete Data can only take certain values. There are distinct or different.
Discrete data is the type of data that has clear spaces between values. Let me put it differently the first column consists of categories of buckets discrete data and the second column consists of kilometers driven continuous data. An extra variable is added and R 2 improves to 052.
The number of objects in a collection. Discrete variables represent counts eg. For a discrete distribution probabilities can be assigned to the values in the distribution - for example the probability that the web page will have 12 clicks in.
Continuous variables represent measurable amounts eg. Let x n x 0 and y n y 0. Discrete variable assumes independent values whereas continuous variable assumes any value in a given range or continuum.
D x y 0 x y 1 x y. Discrete and continuous variables are two types of quantitative variables. Consider the metric space R d where.
The differences are that discrete metrics are usually easier to capture for example by visual inspection why continuous metrics usually require some type of measurement instrument such as a gauge or stopwatch. A discrete variable is always numeric. 7 rows Discrete data is countable.
Discrete Random Variable. The driven kilometers can only be assigned to one of these discrete data buckets. For example the number of customer complaints or the number of flaws or defects.
Unlike a continuous variable which can be indicated on the graph with the help of connected points. Continuous variable Continuous variables are numeric variables that have an infinite number of values between any two values. Key Differences Between Discrete and Continuous Data.
A continuous distribution is one in which data can take on any value within a specified range which may be infinite. If both Y and Xs are continuous then Regression can be used.
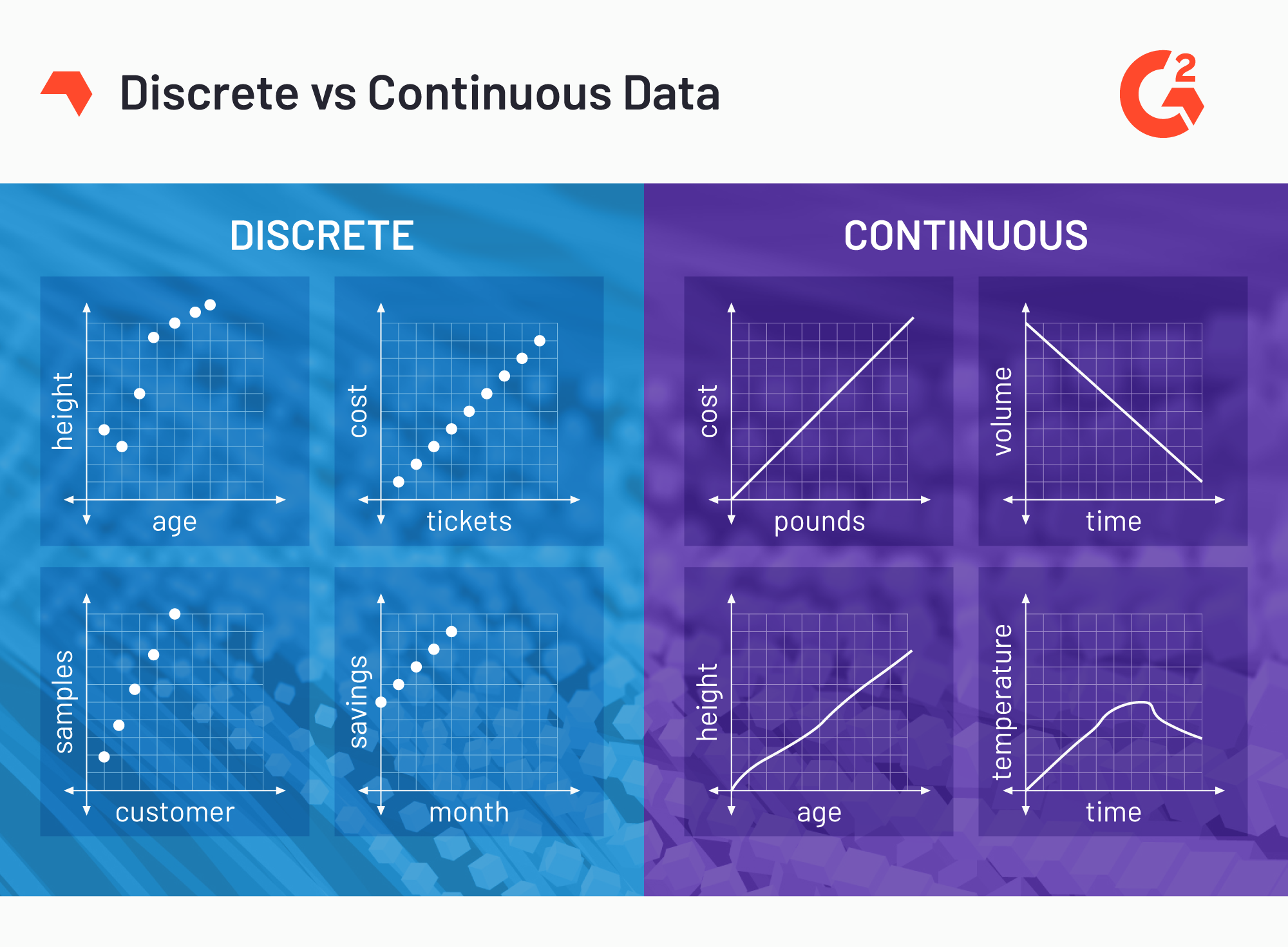
Discrete Vs Continuous Data What S The Difference

Discrete Vs Continuous Time And Discrete Vs Continuous State Space Download Scientific Diagram

4 Types Of Scales For Continuous Discrete Explained With Examples Sixsigmastats
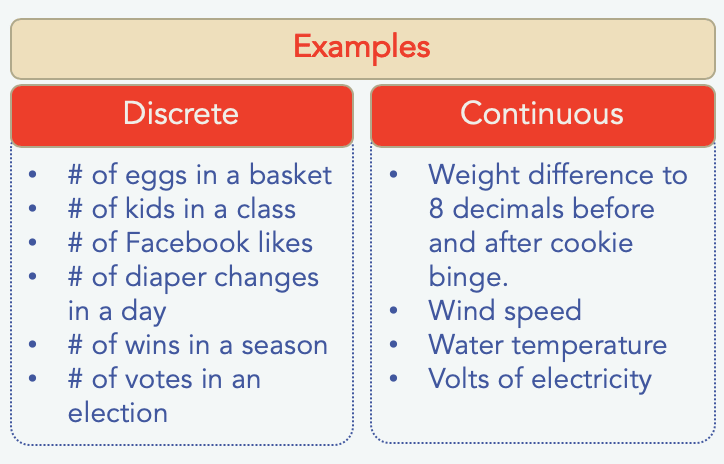
Statistics In Marketing Discrete Probability Distributions Bernard Ml A B
No comments for "Explain the Difference Between a Discrete and a Continuous Metric"
Post a Comment